The way people search online is changing, and it’s changing fast.
Instead of typing into that Google search bar and browsing through ten blue links, users are now asking AI-powered search engines (like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s AI Overviews) and receiving direct, summarised responses.
Today, this is known as AI search, which blends traditional web crawling with large language models (LLMs) that generate conversational responses using web-based information.
For users, it means faster and more intuitive answers.
For small businesses, it means a new kind of visibility challenge. One where getting cited inside AI’s response may become just as important as ranking in search results themselves.
Over the past year, data from multiple analytics platforms has shown that traffic from organic search is plateauing, and in some cases, even declining. This is especially true for industries that rely on informational or local discovery.
AI search is changing not only how consumers find information, but who they find. This is both a disruption and an opportunity.
The rules of online visibility are changing, and they’re changing fast. The shift from keyword search to AI search is rewriting how small businesses get discovered online.
What is AI Search (and Why It’s Different from Traditional Search)
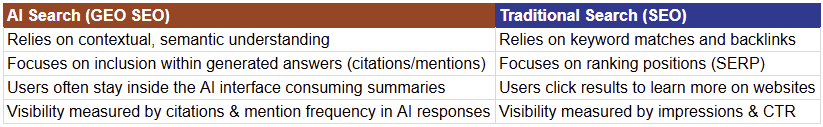
Traditional search engines like Google rank web pages based on their signals such as keywords, backlinks, and content freshness.
AI search refers to AI platforms (like ChatGPT) that use generative AI models to provide contextual, summarised, and conversational answers rather than a simple list of websites.
For example. if you type, “Best plumbers near me” into Google, you’ll get a list of plumbing businesses.
But in AI, a natural language answer would show and sound like this; “Here are some of the most reliable plumbing services near Melbourne, including [business entity], who are known for their quick and friendly expertise.”
That sentence is generated, not copied, but also sourced from the world wide web.
Behind the scenes, the AI model retrieves information from relevant websites, fact-checks it across multiple sources, and then generates a response that may include citations (depending on the platform). Below is an simplified example of the process.
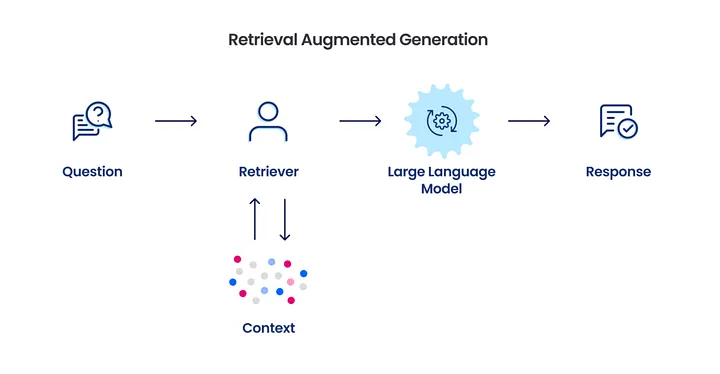
This reminds me of a time when I was in a meeting with a client. They told me they found and purchased a smart watch using ChatGPT alone. They didn’t go to Google or look up reviews. They just asked ChatGPT a series of questions and ended up buying directly from their website.
This small example is a peek into what the future looks like and gives us insights into how our brand visibility strategies should pivot.
This means that your business doesn’t always need to be ranked first to be referenced first. The focus is shifting from keywords to entities. Entities include people, brands, and businesses that AI recognises as an authority on the topic.
Instead of ranking websites by backlinks and keywords, AI search engines pull from trusted entities such as people, brands, and businesses with established authority in their topic.”
How AI Search Changes Discovery
From Rankings to Answers
AI search engines no longer display a list of results the way traditional search does. Instead, they generate direct, conversational answers. These responses often pull information from multiple sources, citing only a few of them.
This shift means that visibility is no longer about ranking first, it’s about being one of the sources chosen for citation within an AI-generated answer.
A New Discovery Funnel
Search behaviour now starts and ends inside the AI interface.
Users ask a question, receive a summary, and often stop there. The traditional path of “query > click > website visit” has been replaced by “query > generated answers > citation (optional) > website visit (optional).”
This new model alters the discovery process and puts great emphasis on machine-readability and trust signals rather than backlinks or keyword density.
How AI Decides Which Sources to Cite
Generative engines select sources differently from Google’s ranking algorithm, and look for information that is;
- Consistent across the web, especially between your website, Google Business Profile, and directory listings.
- Structured with semantic markup, including headings, FAQs, and schema that help models interpret context.
- Fresh and verifiable, with recent updates, statistics, or case studies.
- Entity-rich, meaning your business, products, and services are clearly identifiable and connected to known industry terms.
For example, if a business maintains the same contact details, service descriptions, and service areas on its website and Google profile, AI systems can confidently use that information. Similarly, if your content includes schema like LocalBusiness or FAQPage, it’s easier for models to extract accurate facts.
New Metrics for Visibility
In AI search, impressions and clicks only tell part of the story.
Many users now get their answers without ever visiting a website, so traditional analytics don’t reflect full visibility.
There are two emerging metrics that matter more now;
- Citation Frequency: how often your business is mentioned in AI-generated results.
- Answer inclusion rate: how frequently your content appears as part of AI Overviews or summaries.
Tracking these helps small businesses understand their rech inside AI ecosystems, even when website traffic doesn’t directly show it.
Platforms like Perplexity and ChatGPT are now capable of citing external websites, sometimes giving small publishers the kind of visibility that used to require massive SEO investment.
However, this new ecosystem rewards structured, trustworthy, and machine-interpretable content, not just keyword-optimised pages.
This is where Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO) comes in. This is a new discipline focused on optimising websites for visibility within AI-generated search experiences.
Example Case Study – AI Search with B2B Products
For one of our B2B clients, we optimised their product pages as well as a few key blog posts.
One of the first things we did was meet with their engineers, who often chat directly with prospective customers. Our intention was to identify key paint points and common questions that gets asked.
After identifying the top commonly asked questions (in relation to the product), we updated their FAQs with not only insights from our research, but insights from the engineers themselves.
We then added FAQ schema to the page, tweaked the product descriptions, and a lot more contextual information to the applicable product pages themselves.
We also optimised key blog posts in relation to that product and added internal links with semantically-relevant anchor text.
Below is the result.
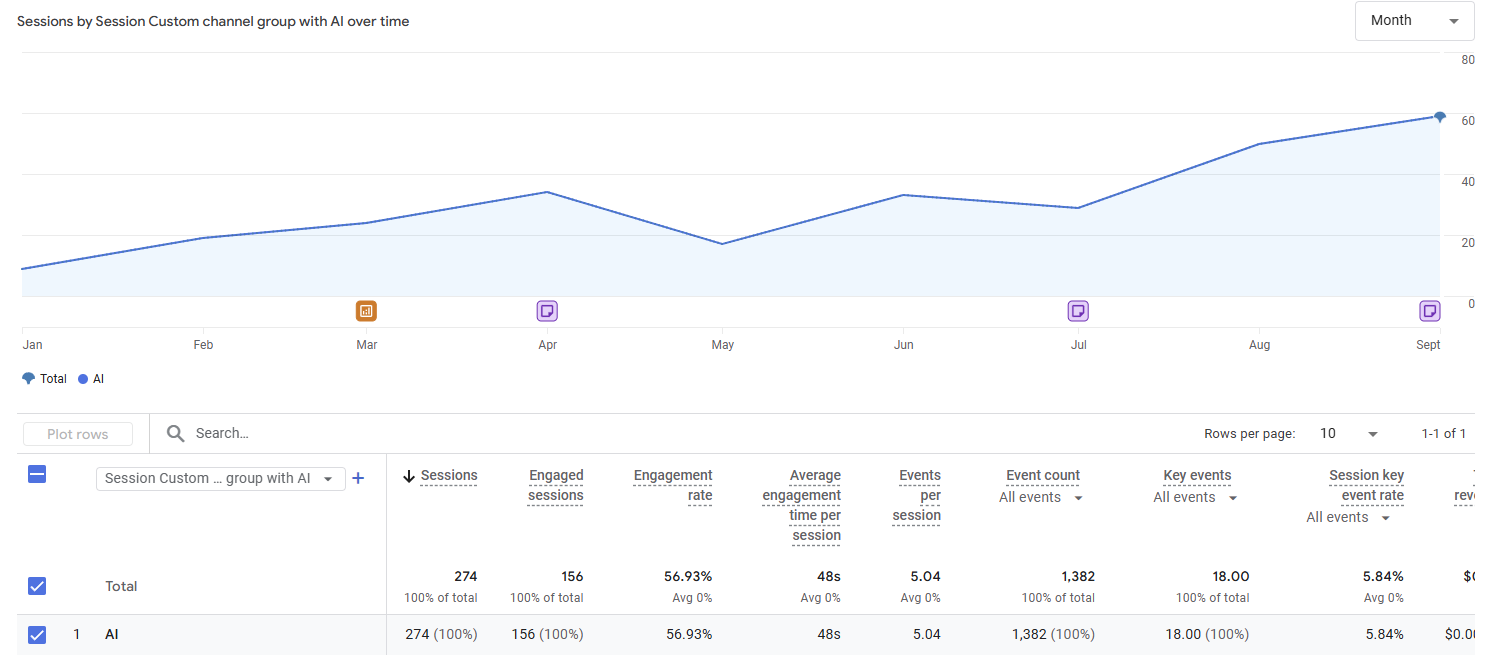
Our implementation took place throughout July, and from what we’ve seen in GA4, AI is sending traffic directly to the product pages and blog posts that we optimised.
Another note is that we’ve been doing their SEO for several years now, sticking to what we know works, which is just the basics. So it makes sense that we were already getting cited by AI prior to these changes.
As a cherry on top, we’ve been able to generate AI-attributed leads for this client, which at the time of this post, is still quite new within the industry.
To summarise what we’ve done for this client;
- We identified unique insights and pain points
- We added these key factors into product pages
- We optimised blog posts to help add contextual relevance
- We added schema markup
How AI Search is Affecting Small Businesses
1. Fewer Clicks from Google
One of the clearest effect of AI search is a decline in website visits.
Google’s AI Overviews‘ generative search feature pulls information from multiple websites to create instant answers. While this improves user experience, it reduces the number of people clicking through to the websites it sourced the information from – which isn’t good when tracking organic traffic.
Below is an example of the impact of AI Overviews on impressions (in purple).
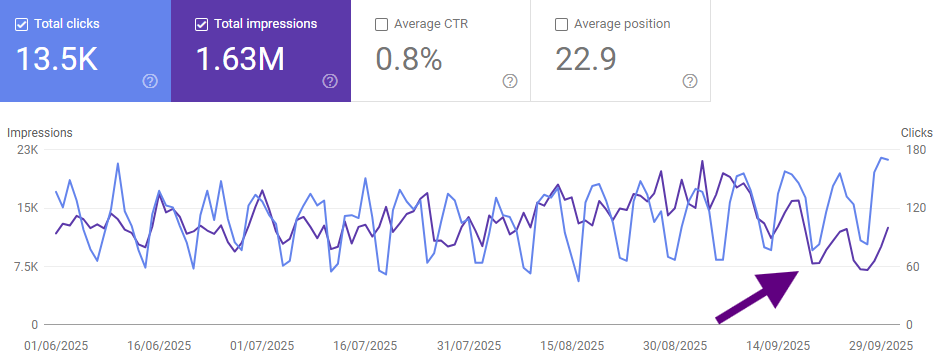
Small businesses that rely only on Google rankings may start to see a gradual decline in traffic, even if they’re still ranking at the top of the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs).
Many of these businesses have noticed that even when their search rankings stay the same, their organic traffic and click-through rates dropped. This means that your decline in organic traffic isn’t due to rankings, it’s because of Google satisfying user intent direclty in the results through AI Overviews.
Larger and more recognised brands often get default preference because their data is widely linked and frequently referenced.
2. Declining Brand Visibility
AI search focuses on delivery facts, not promoting brands.
When LLMs generate answers, they tend to blend data from multiple sources, often without highlighting where that data came from (unless explicitly requested). As a result, businesses can lost exposure even when their information is used.
Instead of showing multiple listings for different providers, AI-generated answers often cite one or two “trusted” sources. That means visibility now depends on whether or not your brand gets cited, not just whether your site is indexed.
Small businesses with weaker brand signals, inconsistent online listings, or limited digital authority are the most at rick of disappearing from this new search experience.
3. Larger Brands Have a Built-In Advantage
Big companies are winning in AI search mainly because their data is easier to understand. They use structured data, are verified across trusted databases, and have extensive media coverage that reinforces credibility.
Aggregators like Yelp, Clutch, TripAdvisor, and ProductReview are also dominating as they provide structured and reliable information at scale, making them “safe” sources for AI models to summarise.
As a result, these platforms are often cited instead of small business websites.
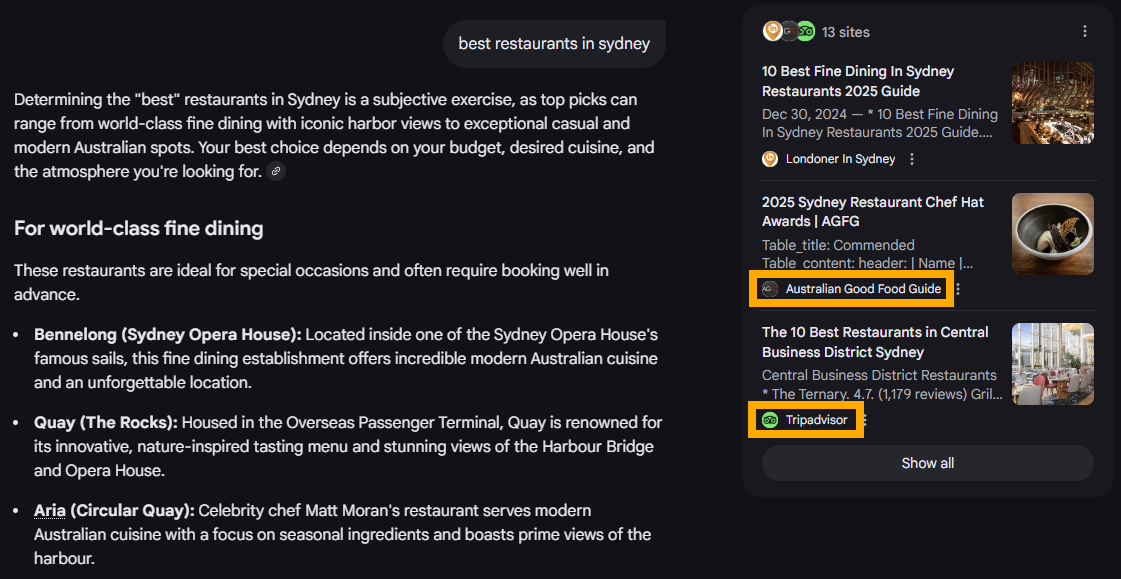
4. Harder to Measure SEO Performance
AI search introduces a visibility gap that traditional analytics can’t track.
You might still see similar impressions in Google Search Console, but clicks and leads decline because users get their answers directly in AI summaries.
Currently, there’s one filter setting within Google Analytics 4 (GA4) that allows you to see which AI brought traffic to your website.
Track AI Traffic in GA4 in 5 Minutes
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to track AI traffic in GA4. We use this with all of our clients to help bridge the information gap and establish a baseline for how AI is impacting their website. It’s free and took us about 5 minutes to set up!
What many industry professionals are doing now is using third-party tools to “track” these new metrics;
- Citation frequency: how often your brand or website is mentioned in AI-generated results.
- Answer inclusion rate: How often your content appears as part of AI Overviews or summaries.
These two metrics alone will help provide a clearer picture of your real digital reach in this growing AI-first world.
5. Local SEO is Now Entity Driven
GEO has turned local SEO into a data validation exercise.
With traditional SEO, backlinks and reviews were high on the priority list (and they’re still very important today!). Now with AI, LLMs cross-check details about your business across the web.
They compare your Google Business Profile, website, and directory listings to ensure everything matches.
If your service areas, hours, or business descriptions don’t align across platforms, your business might be ignored entirely.
6. Structured, Credible Content Wins
Businesses that publish verifiable, structured, and experienced-based content are better positioned to appear in AI-generated responses.
Search engines and LLMs look for evidence that information is reliable and grounded in real-world expertise (which was a main contributing factor to our client mentioned above!).
This means adding schema markup, updating service pages with transparent details, and including data that models can fact-check.
Original case studies, visuals, and proof-based content all make your pages easier to cite.
The Rise of GEO
Traditional SEO focuses on rankings, while GEO (Generative Engine Optimisation) focuses on citations and authority. AI search isn’t replacing traditional SEO, it’s rewriting the rules.
Small businesses that continue relying only on keyword-based SEO risk losing their customers to competitors.
This change doesn’t have to be a disadvantage. It’s an opportunity to build stronger foundations.
By keeping your website structured, your data consistent, and your content credible, you make it easier for both humans and AI systems to trust your brand.
Our team helps businesses adapt to this changing landscape by making their content readable and trustworthy to both humans and machines.
Contact us and learn how to optimise your website for AI search.
